Languages of India
With nearly 1600 languages and dialects, India is one of the most diverse countries in the world linguistically. 22 of them are officially recognized by the Indian Constitution.
The languages of India primarily belong to two major linguistic families:
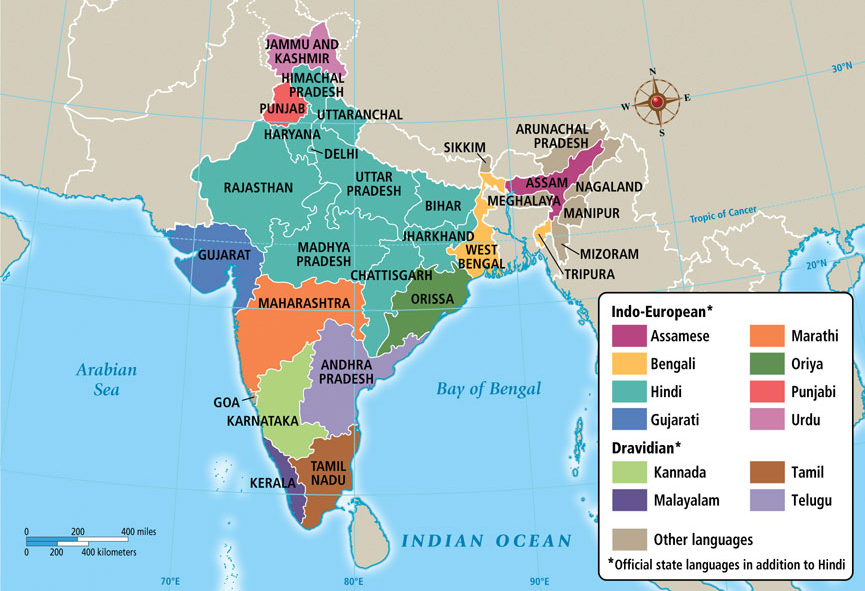
- Indo-Aryan languages (the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European family) spoken by 74% of the population, mainly in the north. The most important is the Hindustani (Hindi and Urdu, about 240 million people). They were brought into India from the northwest during the second millennium B.C., the Indo-Aryan tongues spread throughout the north, gradually displacing the earlier languages of the area.
- Dravidian languages spoken by 24% of the population. Most Dravidian speakers reside in South India, where Indo-Aryan influence was less extensive than in the north. Only a few isolated groups of Dravidian speakers, such as the Gonds in Madhya Pradesh and Orissa, and the Kurukhs in Madhya Pradesh and Bihar, remain in the north as representatives of the Dravidian speakers who presumably once dominated much more of South Asia. The most commonly used Dravidian languages are Telugu (Andhra Pradesh), Tamil (Tamil Nadu), Malayalam (Kerala) and Kannada (Karnataka).
The others languages, around 2% of the population, are the Sino-Tibetan and Austroasiatic languages mostly spoken by tribal people. Sino-Tibetan speakers live along the Himalayan fringe from Jammu and Kashmir to eastern Assam. The Austroasiatic languages are spoken by groups of tribal people from West Bengal through Bihar and Orissa and into Madhya Pradesh.
In addition, the Government of India has awarded the distinction of classical language to Tamil, Sanskrit, Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam and Odiya.
As a former colonial language, English serves as the lingua franca in India. It is used by many authors and is a major administrative language.
The Constitution of India does not give any language the status of national language.The official language of the Union Government of the Republic of India is Hindi in the Devanagari script (alphabet of India and Nepal).
The Constitution of India recognizes 22 languages:
- Assamese (Assam, Arunachal Pradesh)
- Bengali (West Bengal, Tripura, Assam, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Jharkhand)
- Bodo, sino-tibetan (Assam, West Bengal, Meghalaya)
- Dogri (Jammu & Kashmir)
- Gujarati (Gujarat, Dadra & Nagar Haveli et de Daman & Diu)
- Hindi (Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand)
- Kannada (Karnataka, Goa. Minority in Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh , Maharashtra)
- Kashmiri (Jammu & Kashmir)
- Konkani (Goa, Maharashtra, Karnataka)
- Maïthili (Bihar)
- Malayalam (Kerala, Lakshadweep)
- Meitei (Manipur)
- Marathi (Maharashtra, Goa, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Karnataka)
- Nepali (Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam)
- Oriya (Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh)
- Urdu (Jammu & Kashmir, Telangana, Delhi, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh)
- Punjabi (Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu, Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand)
- Sanskrit
- Santali Santhal tribals of the Chota Nagpur Plateau (comprising the states of Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha)
- Sindhi, Sindh (now in Pakistan, Rajasthan, Kutch, Gujarat)
- Tamoul (Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh)
- Telegu (Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Odisha)






